Learn about Solar Power Generation System with Diagram
In this article, we are going to learn about the Solar Power Generation System with Diagrams. We will learn about On Grid, Off Grid, and Hybrid systems. We will learn what are the main components and how it works. An On-Grid Solar Power Generation System is also known as a Grid-Tied Solar System or Grid-Connected Solar System. It is basically a renewable energy setup that harnesses solar energy to generate electricity and feeds it directly into the local power grid. This system is designed to work in conjunction with the existing utility grid infrastructure.
On-Grid Solar Power Generation Systems are suitable for a wide range of applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings. For example, many homeowners install on-grid solar systems on their rooftops to generate electricity for their own consumption. The excess electricity can be fed back into the grid, earning them credits through net metering.
The primary difference between solar power generation by large-scale solar plants and solar power generation by individual homeowners and small producers lies in the scale, purpose, and complexity of the installations. But the concept of actual power generation, conversion, storage, transmit are the same.
Solar Power Generation System Diagram
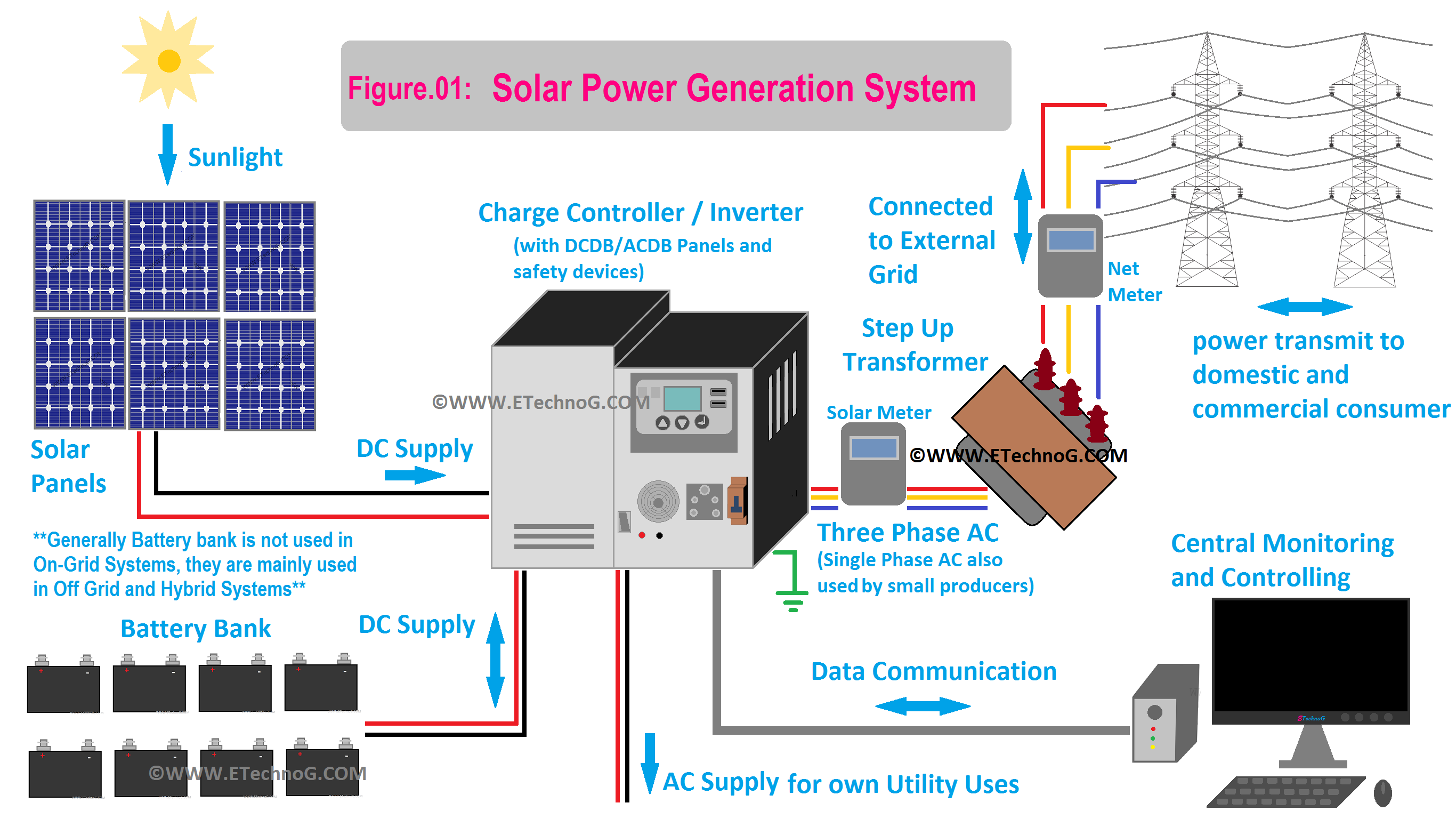
First of all, let's see the structural diagram that shows a basic overview of the Solar Power Generation System.
In the above diagram, we have shown a Hybrid setup which means it is a combination of On Grid and Off Grid system. If you want to see this diagram for an Off-grid system then ignore the meters, transformer, etc. And if you want to see this diagram for an On-grid system then ignore the battery banks and charge controllers.
Difference between On-Grid, Off-Grid, and Hybrid Solar Power Systems,
On-Grid System: This setup connects your solar panels to the regular power grid. It saves you money on your electricity bills by using solar power when the sun shines and selling any extra power back to the grid. But, if the grid goes down, your solar panels won't provide power.
Off-Grid System: With this system, your solar panels provide all your power. You store extra energy in batteries to use at night or when it's cloudy. It's great for places where there's no regular power grid, but you need to manage your energy carefully.
Hybrid System: This system combines the best of both worlds. Your solar panels are connected to the grid, so you can use grid power when you need it and sell excess solar power. Plus, you have batteries for backup during power outages or when the sun isn't shining.
Main Components
Here is the list of main components used in a Solar Power Generation System,
- Solar Panels
- Charge Controller
- Inverter
- Distributions Boards(DCDB / ACDB) and Safety Devices
- Battery Bank
- Transformer
- Monitoring and Control Systems
- Solar Meter
- Net Meter
Solar Panels (Photovoltaic Modules)
These are the primary components that capture sunlight and convert it into electricity using the photovoltaic effect. They basically generate electricity in the form of Direct Current or DC. They are installed on rooftops or other suitable areas. The small producers such as homeowners install solar panels on their rooftops but the solar plants use substantial open land or suitable areas to accommodate a large number of solar panels and associated infrastructure.
Charge Controller
A charge controller is also a very important component in the solar power system. They are basically used to charge the batteries. A charge controller is basically used in off-grid and hybrid solar systems, but it's not typically used in on-grid solar power systems. Since on-grid systems are directly connected to the utility grid, they don't require a charge controller. The charge controller is used to manage the charging and discharging of batteries, which is a feature of off-grid or hybrid setups.
Inverter
The DC electricity generated by the solar panels needs to be converted into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is what our homes and the grid use. An inverter is used to perform this conversion. There are various types of inverters available, including central inverters, string inverters, and microinverters.
In large solar power plants, DC to Three-Phase inverters are used where the inverter takes the DC supply from the battery and converter it into a three-phase supply. The large solar plant supplies power to the grid in the form of a three-phase AC supply. But the small setup used by the small producers generally uses Single Phase inverters and they supply the power supply to the grid in the form of single-phase AC supply.
Distributions Boards(DCDB / ACDB) and Safety Devices
Distribution Boards (DBs), specifically DC Distribution Boards (DCDB) and AC Distribution Boards (ACDB), along with safety devices, play a crucial role in ensuring the safety, functionality, and efficiency of solar power generation systems.
In a solar power system, multiple solar panels are connected in strings to generate DC electricity. The DCDB allows for proper distribution and management of these DC circuits, ensuring that the electricity generated by each string of solar panels is routed correctly. DCDBs include switches or circuit breakers that can isolate individual strings or panels. This is important for maintenance, troubleshooting, and safety purposes. DCDBs often include fuses or circuit breakers that protect the wiring and components from overcurrent conditions, which can occur due to faults or malfunctions in the system.
ACDBs manage the connection of the inverter(s) to the building's electrical panel and the grid. They ensure that the AC power generated by the solar panels is properly integrated into the building's electrical system. ACDBs include circuit breakers or switches that can disconnect the inverter from the electrical panel for maintenance or safety reasons.
Other different types of safety devices such as Ground fault protection devices monitor the system for any leakage of current to the ground. They trip the circuit if a ground fault is detected, preventing electric shock hazards. Lighting Arrester provides protection against lightning. In the small solar setup, all of these panels and safety devices may not be used.
Battery Bank
A battery bank is a collection of interconnected batteries that store electrical energy for later use. In solar power generation systems, battery banks are commonly used in off-grid and hybrid setups to store excess energy generated by solar panels during periods of high sunlight for use when the sun is not shining, such as during the night or on cloudy days. In hybrid systems, battery banks can provide backup power during grid outages, ensuring continuous electricity supply to critical loads.
Transformer
In solar power systems, a transformer can be used in certain configurations to step up or step down the voltage of the electricity generated by the solar panels or inverters. Step-up transformers are used to increase the voltage of the electricity generated by the solar panels before it is fed into the grid. This can be useful in cases where the local grid requires a higher voltage level than what the solar panels produce. Increasing the voltage reduces line losses during transmission, making it more efficient to transfer electricity over longer distances. But if the voltage level of the power generation station and the grid is the same then there is no need for a transformer.
Monitoring and Control Systems
Monitoring and control systems are essential components of solar power generation systems that provide real-time visibility, management, and optimization of the system's performance, energy production, and various parameters. These systems help ensure the efficiency, safety, and reliability of the solar power setup. Monitoring systems collect real-time data on parameters such as solar panel output, inverter performance, battery status (if applicable), energy consumption, and grid interactions. Many monitoring systems allow users to access the data remotely through web interfaces or mobile apps. This enables users to monitor their system's performance from anywhere.
Solar Meter and Net Meter
Solar Meter is an important component of the system. That is basically a bi-directional electricity meter. This meter measures the electricity produced by the solar panels as well as the electricity consumed by the grid. When the solar panels produce more electricity than is being consumed, the excess is fed back into the grid.
Many regions implement a net metering system. When the solar panels generate more electricity than the building's immediate needs, the excess electricity is sent back to the grid, and the meter runs in reverse. This allows the building owner to earn credits for the excess electricity that can be used to offset electricity consumption during periods when the solar panels aren't producing enough electricity (e.g., nighttime).
Read Also: